Rotavirus infection: symptoms, diagnosis treatment in Kiev
Rotavirus infection is a disease caused by the rotavirus virus, which attacks the human gastrointestinal tract. This virus often leads to acute gastroenteritis, which is manifested by symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and general weakness. The disease is caused by contact with infected people or objects, or by consuming contaminated food or water. Rotavirus is often spread in poor hygiene or in crowded places such as kindergartens or hospitals.
What is a rotavirus? Rotaviruses are non-enveloped RNA viruses belonging to the family Reoviridae. The viral nucleocapsid consists of 3 concentric envelopes that enclose 11 segments of double-stranded RNA.
In simple words Rotavirus is a virus that causes acute inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract known as rotavirus infection. This virus is one of the most common causes of viral gastroenteritis in children and adults worldwide. Rotavirus is transmitted through contact with infected people or through contaminated objects and surfaces. It can cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, animal pain and fever. Rotavirus infection is usually self-limited, but in some cases medical attention may be needed to prevent dehydration (dehydration of the body) and other complications.

There are several types of rotaviruses, but the main type that causes illness in humans is group A rotaviruses. They are the most common and are responsible for most cases of rotavirus infection in humans. Groups B and C can also cause illness, but their occurrence is much lower compared to group A. Each of these types of rotavirus has its own subtypes and strains that can cause different forms of the disease with varying degrees of severity
.
Symptoms of rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection presents with a variety of symptoms that usually begin to appear within a few days of infection. The main symptoms include vomiting, which is frequent and intense and may last for several days. Diarrhea, which may be watery or contain intestinal discharge, is also characteristic. Patients often experience abdominal pain that can be severe and spastic. Other symptoms include general weakness, appetite disorders, and low body temperature. In children, the disease can lead to dehydration due to frequent vomiting and diarrhea, requiring medical intervention.
Rotavirus: Symptoms of rotavirus infection in tableRotavirus: Symptoms of rotavirus infection in table
| № | Symptom | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vomiting | Recurrent episodes of vomiting, often intense and may last for several days. |
| 2 | Diarrhea | Watery or loose stools, often accompanied by frequent trips to the toilet and fluid loss. |
| 3 | Abdominal pain | Severe and spastic pain in the abdominal region, often accompanied by an unpleasant sensation in the intestines. |
| 4 | General weakness | Loss of strength, deterioration of general health and possible performance problems. |
| 5 | Appetite disorders | Loss of appetite or feelings of disgust for food, which can lead to additional eating problems. |
| 6 | Low body temperature | A drop in body temperature, which can be a sign of infection and inflammation. |
| 7 | Dehydration in children | A particularly dangerous condition for children, characterized by fluid loss due to frequent vomiting and diarrhea, requiring immediate treatment. |
| 8 | Headache | Feeling pain or pressure in the head area, which may be caused by general malaise and dehydration. |
| 9 | Muscle pain | Muscle soreness that may accompany general weakness and fatigue. |
| 10 | Fatigue | Feeling tired or sleepy, usually associated with general illness and dehydration. |
Diagnosis of rotavirus infection
Diagnosis of rotavirus infection is usually based on the clinical manifestations and symptoms of the disease. The physician may examine the patient and inquire about the patient’s medical history, including contact with possible sources of infection. Laboratory tests, such as stool tests for rotavirus or immunodiagnostics to detect antibodies to the virus in the blood, may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, additional testing may be required, especially if symptoms are equivocal or complications are present.
Description of the disease
Before the advent of rotavirus vaccines, this virus was the leading cause of serious cases of gastroenteritis in infants and young children. Vaccination against rotavirus infections has led to a dramatic reduction in the number of infections and transmission in the vaccinated population, and norovirus is now the most common pediatric viral gastroenteritis. Symptoms of rotavirus infection can range from mild watery diarrhea of limited duration to severe diarrhea with vomiting and fever, which can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and, rarely, death. After an incubation period of 1-3 days, the disease often begins suddenly, and vomiting often precedes the onset of diarrhea. Gastrointestinal symptoms usually resolve in 3-7 days. Severe cases of rotavirus infection are more common in unvaccinated children between 3 and 35 months of age.
Treatment of rotavirus infection
Treatment of rotavirus infection is usually aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing dehydration. Drug therapy includes taking antiemetics and antidiarrheals to reduce vomiting and diarrhea. Medications to reduce fever and relieve pain may also be used. Intravenous fluids and electrolytes may be required for children and those at high risk of dehydration.
An important aspect of non-medication therapy is to maintain hydration through frequent fluid intake such as water, juices or electrolyte solutions. Patients are also advised to rest and limit physical activity for rapid recovery. The key to non-medication therapy is to follow dietary recommendations, avoiding heavy and fatty foods to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
Rotavirus infection is usually treated by a pediatrician or internist. In the case of children, a pediatrician who specializes in treating children and adolescents is often consulted. A general practitioner may also treat rotavirus infection in adults. In some cases, especially in case of complications or severe course of the disease, consultation with an infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist may be required.
Treatment for rotavirus infection usually involves several steps:
- Symptomatic treatment: Primarily aims to relieve symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and general malaise. The doctor may prescribe antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and fever and pain relievers.
- Hydration: It is particularly important to maintain body fluid levels to prevent dehydration, especially in children. This may include administration of oral re-hydration solutions or, in severe cases, intravenous fluids and electrolytes.
- Diet: A light diet is recommended, avoiding fatty, spicy and heavy foods that can irritate the gastrointestinal tract. It is recommended to consume easily digestible foods such as broths, broths, rice and toast.
The duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity of the disease and the individual patient. Usually, symptoms begin to improve within a few days of treatment, and full recovery may take a few days to a week. However, in some patients with complications or compromised immune systems, recovery may take longer.
Pediatric rotavirus infection
Rotavirus in children has several features compared to the disease in adults.
- A higher risk of dehydration: Children have a higher risk of dehydration due to a higher frequency and intensity of vomiting and diarrhea. This is especially important in infants and young children who may have limited ability to drink adequate amounts of fluids.
- More severe course of illness: Children often have a more severe course of infection than adults. They may experience more severe symptoms such as fever, severe vomiting and diarrhea, which can lead to severe weakness and dehydration.
- Frequent cases: Rotavirus infection is one of the most common causes of acute gastroenteritis in children. In pediatric populations such as kindergartens and schools, the incidence can be particularly high because of the ease of transmission from one child to another.
- Special attention to hygiene is required: Because rotavirus is highly infectious, it is important to practice good hygiene, especially in children. Regular hand washing with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the toilet, can help prevent transmission.
Rotavirus infection in adults
Adults show similar symptoms as children, but they usually have some peculiarities:
- Symptoms: In adults, rotavirus infection may present with severe vomiting, profuse diarrhea, abdominal pain, and general weakness. Adults may also experience headache, muscle aches, and fatigue.
- Duration: In adults, symptoms of rotavirus infection are often longer lasting than in children and may last from a few days to a week.
- Treatment: Treatment of rotavirus infection in adults usually includes symptomatic therapy to relieve symptoms. Your doctor may recommend taking antiemetics and antidiarrheal medications, as well as medications to reduce fever and relieve pain. It is also important to maintain hydration by drinking enough fluids and following a light diet. In some cases, intravenous fluids and electrolytes may be required, especially if there is a risk of dehydration.
Complications
Rotavirus infection can lead to various complications in both children and adults. Here are some of them:
- Dehydration: One of the most serious complications of rotavirus infection is dehydration, especially in children. Loss of large amounts of fluid through frequent vomiting and diarrhea can lead to serious consequences such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
- Electrolyte imbalance: Loss of fluids and electrolytes due to vomiting and diarrhea can lead to electrolyte imbalance in the body, which can cause complications such as cardiac arrhythmias and muscle cramps.
- weakened immune system: Rotavirus infection can lead to a weakened immune system, which can increase the risk of developing other infections and complications in the future.
- The occurrence of co-infections: In some cases, the infection may open the way for the development of other infections, such as food poisoning or pneumonia.
- Psychological effects: In children and adults, rotavirus infection can cause stress and anxiety because of the need to limit contact with others, as well as because of unpleasant symptoms and prolonged recovery.
All these complications emphasize the importance of timely treatment and monitoring of patients with rotavirus infection, especially in children and those with weakened immune systems.
Vaccination against rotavirus infection

Vaccination is an effective way to prevent rotavirus infection and its complications. The vaccine helps protect the body from contracting the virus and reduces the risk of developing the disease. Here’s how vaccination plays an important role in fighting rotavirus infection:
- Prevention of disease: Vaccination helps reduce the risk of rotavirus infection in vaccinated persons. This is especially important for children, in whom rotavirus infection can be severe.
- Reduces severity of illness: Even if a vaccinated person does contract rotavirus, the vaccine can make the course of the disease milder and reduce the risk of complications such as dehydration.
- Prevention of complications: Vaccination helps prevent the development of complications of rotavirus infection such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and other serious conditions, especially in children.
- Reducing treatment costs: The introduction of rotavirus vaccination reduces the costs of treating the disease, including medical care, hospitalization, and medications.
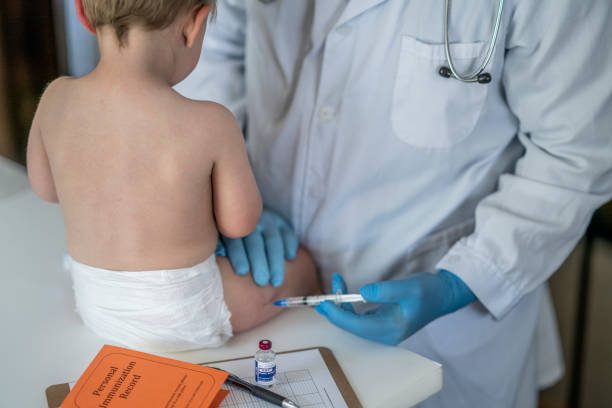
Rotavirus vaccination is an important public health intervention that helps protect people from this common and potentially dangerous disease.
Diet and hydration in rotavirus infection
Proper nutrition and increased fluid intake play an important role in the treatment of rotavirus infection.
- Diet: In rotavirus infection, a light to moderate diet is recommended, avoiding heavy, spicy and fatty foods that can irritate the gastrointestinal tract. Easily digestible foods such as broths, broths, rice and toast are preferred. Small portions of food are recommended to be eaten frequently so as not to overload the stomach.
- increase fluid intake: It is important to ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration. Drinking plenty of water, juices, decoctions, tea, or special oral solutions for hydration is recommended. In case of severe vomiting and diarrhea, it is recommended to consume fluids in small portions to avoid overloading the stomach.
Importance of hygiene
Keeping clean and practicing good hygiene plays an important role in preventing the spread of rotavirus infection.
- Frequent hand washing: One of the most effective ways to prevent transmission of rotavirus is to wash hands frequently with soap and water. It is especially important to wash your hands before eating, after using the toilet, and after contact with infected material.
- Use of antiseptic hand sanitizers: If it is not possible to wash your hands, alcohol-based hand sanitizers can be used to disinfect your hands.
- Avoiding close contact with sick people: It is important to avoid close contact with people with rotavirus infection, especially during the first few days of illness when the risk of transmission is highest.
- Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces: Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, especially those that may be contaminated with vomit or feces, is also important to prevent the spread of infection.

Rotavirus infection: myths and facts
Rotavirus infection is often surrounded by myths and misunderstandings. Let’s look at common misconceptions about this disease:
- Myth: Rotavirus can be treated with antibiotics. Fact: It is caused by a virus, and antibiotics cannot treat viral infections. Treatment focuses on symptomatic therapy and maintaining hydration.
- Myth: Rotavirus only affects children. Fact: It can affect people of any age. Although children often get this infection, adults can also be infected.
- Myth: Rotavirus infection can only be transmitted through food or water. Fact: Rotavirus can be transmitted through airborne droplets from coughing or sneezing of infected people, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Myth: After a rotavirus infection, a person becomes immune to the virus. Fact: Because there are several strains of rotavirus, infection with one strain does not provide complete protection against other strains. Therefore, reinfection is possible.
- Myth: Rotavirus is not dangerous and does not require medical attention. Fact: In some cases, it can cause serious complications, especially in children and immunocompromised individuals. Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance may require medical attention
- Myth: Seasonal distribution of rotavirus infections. Fact: Rotavirus infections are more likely to occur during certain times of the year, making the disease typical of the winter months in some regions. However, recent research suggests that the seasonality of rotavirus infections may be broader and not limited to winter.
- Myth: Humans can get rotavirus from an animal. Fact: Several animal species, such as monkeys, cows, horses, pigs, and sheep, can contract rotavirus infection and show symptoms of rotavirus diarrhea. However, the typical types of rotavirus in animals are different from those that typically affect humans. Although related strains of rotaviruses have been found in animals and humans, animal-to-human transmission is rare. Most human rotaviruses that share genetic similarities with animal rotaviruses are produced by exchange of virus genes during mixed infection.

Psychological aspects
Rotavirus infection can have a significant impact on the mental state of the patient. Here are some of the psychological aspects of this disease:
- Stress and anxiety: Painful symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and general weakness can cause stress and anxiety in patients. They may fear for their health and worry about possible complications.
- Social isolation: Patients with rotavirus infection often avoid contact with others for fear of transmission. This can lead to social isolation and feelings of loneliness.
- Negative Emotions: Painful symptoms and limitations in daily life can cause negative emotions such as irritation, frustration, and depression.
- Family and loved ones concerns: Patients often worry about the health of their loved ones and fear that they will contract a rotavirus infection. This can cause additional stress.
- Effects on quality of life: Rotavirus infection can temporarily limit a patient’s activities and impair their quality of life. It can cause feelings of helplessness and dissatisfaction.

To cope with the psychological aspects of rotavirus infection, it is important to provide support from family and loved ones, seek medical attention when needed, and adhere to the doctor’s recommendations for treatment and hygiene.
Rotavirus infection is a serious disease that can have serious consequences, especially in children and immunocompromised individuals. In this article, we have looked at various aspects of this disease, from its symptoms and diagnosis to treatment and prevention methods.
It is important to remember that the infection can be dangerous, especially for young children, and requires careful attention and timely treatment. Good hygiene, vaccination and proper nutrition and hydration can help prevent infection and spread of this virus.
In addition, there is a need to advance research on rotavirus infection, including the study of its interaction with stem cells, which may lead to new treatments and prevention methods.
How do I get tested for rotavirus in my body?
There are two main methods of diagnosing rotavirus infection:
Stool analysis:1. Stool analysis:
- This is the most common method of diagnosing rotavirus infection.
- A small stool sample should be collected in a sterile container for analysis.
- The fecal container must be brought to the laboratory within 24 hours.
- Test results are usually ready within 1-2 days.
Blood work:2. Blood work:
- This method is used less frequently than fecal analysis.
- Blood tests can determine the presence of antibodies to rotavirus.
- This method can be used to diagnose rotavirus infection in people who have no symptoms.
Before taking a rotavirus test, you should:
- Consult a physician.
- Provide your doctor with information about your symptoms and medical history.
- Follow the rules for preparing for the test that your doctor will give you.
The results of the rotavirus test will help your doctor:
- Confirm or refute the diagnosis of rotavirus infection.
- Determine the severity of the disease.
- Prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is important to note that this information is for informational purposes only. You should always consult your doctor before deciding whether to take a test for rotavirus.
It is important to note that Coolaser Clinic DOES NOT TEST or TREAT rotavirus infections. This information is for informational purposes only. You should always consult with your physician before deciding to have a rotavirus test.
Therefore, Coolaser Clinic urges all readers to take note of this information and follow the recommendations for prevention and treatment of rotavirus infection. Remember the importance of hygiene, immunization and seeking medical attention when necessary. Taking care of our own health and the health of those around us is a common endeavor.
Sources:Sources: