Treatment of diabetes mellitus and its consequences in Kiev
Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the body cannot properly digest carbohydrates (sugar and starch), the body’s main sources of energy.

Normally, digestion breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, a sugar that is absorbed into the blood.
When blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas, located in the upper half of the abdomen, is activated and releases the hormone insulin. Insulin lowers the concentration of glucose in the blood by transporting it to the body’s cells, where it is used as fuel, or to the liver, where it is stored to be used for fuel when needed.
If the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the body cannot use the insulin it does produce, diabetes occurs. Blood sugar concentrations rise because glucose is not being consumed by the cells. The kidneys begin to excrete sugar in the urine, which is not normal.
External signs of diabetes mellitus photo:

Types of diabetes mellitus
There are two main forms of diabetes. Type T, insulin-dependent, is caused by a defect of unknown origin in the islets of Langerhans, the part of the pancreas that produces insulin. Even very young children can develop this form of diabetes.
In type T, insulin-independent diabetes, the pancreas functions normally, but the body cannot use insulin effectively. Ino da cells lack insulin receptors (protein molecules on the cell surface that insulin sits on to activate glucose transport from the environment to the cell), and insulin just floats around in the blood instead of working properly.

Often obesity, which impairs insulin regulation of glucose transport, contributes to this condition. Because type II most often appears in people after age 40, this form can arise from a gradual slowing of insulin formation in the pancreas. In addition, other endocrine disorders (other glands that secrete hormones into the blood) also disrupt insulin regulation.
Studies show that people with type L diabetes have an inherited tendency toward the disease, The frequency is higher in women, but the chance of adults getting type II doubles every 10 years after age 40.
Some women start diabetes during pregnancy. After childbirth, the disease usually disappears. However, women with signs of diabetes during pregnancy who give birth to babies weighing more than 4,500 g are more likely to develop diabetes later in life.
Symptoms of diabetes mellitus

Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, visual impairment, fainting, irritability, slow healing of cuts and scratches. The patient becomes thin despite constant hunger and large amounts of food eaten.
The same symptoms are found in type II diabetes or no symptoms at all. Doctors often detect this form in routine urine tests.
Diagonosis
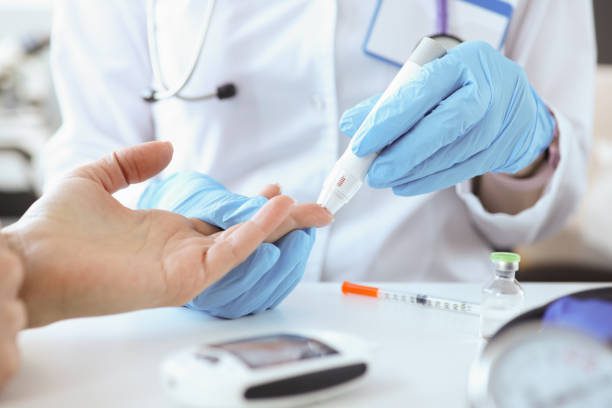
If there are no obvious symptoms, the doctor may diagnose diabetes by blood tests (increase in sugar concentration) and urine tests (appearance of sugar). Sometimes insulin in the blood and ketones in the urine are measured. Ketones are the end products of the breakdown of fat used as an energy source.
Because diabetic patients cannot use glucose normally, the body begins to burn fat and ketones in the urine increase.
Complications
People with diabetes usually control their condition, but untreated diabetes can lead to severe complications. Extremely high blood sugar levels put a strain on other organs. Diabetes activates atherosclerosis, making the arteries that carry blood throughout the body stiffer and narrower.
Diabetes causes insufficient blood supply, which contributes to heart attack, stroke, kidney and eye disease (retinopathy), impaired potency, tissue death due to insufficient blood supply, gangrene and even death.
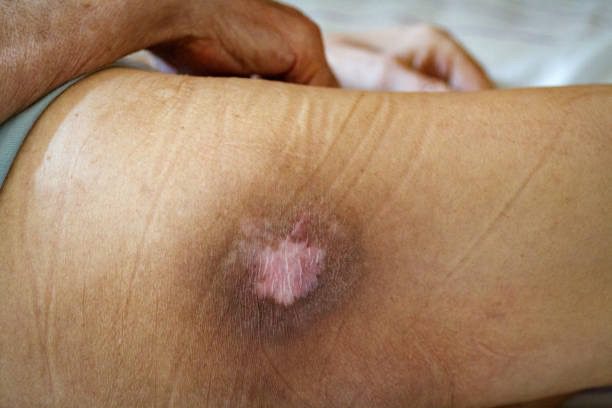
Signs of diabetes mellitus
| sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequent urination | Increased urination |
| Thirsty | Intense desire to drink water |
| Fast weight loss | Involuntary weight loss |
| Fatigue | Constant feeling of fatigue |
| Elevated blood sugar | Blood glucose levels are higher than normal |
| Obesity | Excessive accumulation of fat in the body |
| Diabetic foot | Complication resulting in leg damage |
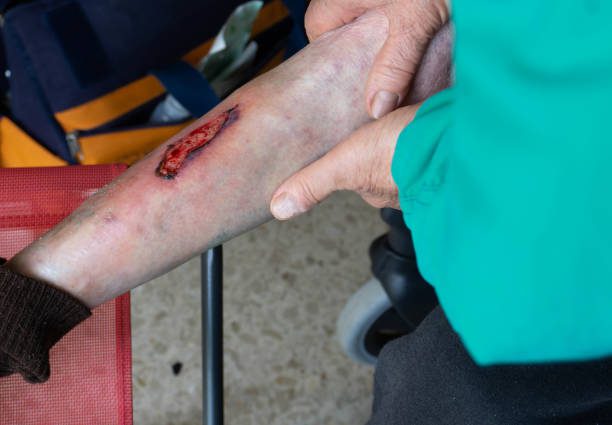
Both forms of diabetes require treatment that ensures normal and constant blood glucose levels. If blood glucose is under control with insulin shots, diet or medication, the patient can lead a normal life.
Diabetes mellitus treatment
Our clinic has been successfully conducting stem cell treatment for diabetes

Type 1, or insulin-dependent diabetes, requires insulin injections to keep blood sugar at the same level throughout the day. If glucose concentrations rise, the body signals weakness, fatigue, and thirst. This means that it is necessary to increase the dose of insulin.
But if the sugar drops too low, the insulin reaction begins: dizziness, hunger, weakness, headache, sweating, trembling. In severe cases – loss of consciousness. A quick solution to the problem is to eat some sugar, such as candy or biscuits.
Ideally, the doctor can prevent such sugar fluctuations by adjusting the type and schedule of insulin injections according to the food intake and energy content of the food. A special diet is important. Young children with diabetes especially need extra calories for growth and normal development. The need for insulin in type 1 diabetes varies greatly from person to person.
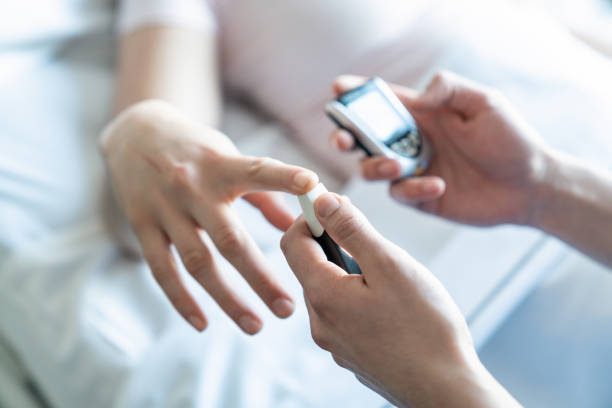

One insulin injection before breakfast is enough for some people, while others need several injections a day. Moreover, the need for insulin changes with age, after surgical operations, during pregnancy and other diseases.
The majority of patients with type T, or insulin-insufficient diabetes, can regulate their condition with the help of a proper diet. Anti-diabetic drugs in pill form are sometimes prescribed, which stimulate the pancreas to make more insulin or make the body more sensitive to its effects.
How to control diabetes

Calculate the cost of Diabetes stem cell treatment
Leave your details and we will contact you for an accurate surgery estimate

A carefully designed diet is necessary to control the disease. For obesity, weight loss diets are recommended. Then the focus is mainly on nutrient balance. Fats are restricted to reduce the chance of atherosclerosis, as well as simple sugars.
Foods include plenty of fiber-filling fruits, vegetables, and whole grains; fiber reduces or slows the absorption of sugar in the digestive tract.

Your doctor provides an approved food regimen that is flexible enough to adapt to your family’s diet.
With any type of diabetes, it is important to monitor the patient’s condition by monitoring blood and urine sugars. More and more often patients themselves conduct such tests at home and adjust insulin doses accordingly. This allows the patient to lead a normal life.
List of literature used:
- diabetes.org
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: What is Diabetes?
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: What is Diabetes?
Coolaser Clinic treats diabetes in Kiev on Pechersk, as well as treat its consequences, in the form of diabetic foot and non-healing wounds stem cells.