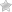What is the danger of melanoma, its causes and consequences
What is melanoma? You need to know the answer to this question because it is one of the most dangerous forms of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing the pigment melanin. These cells give our skin its color and protect it from the effects of ultraviolet radiation. However, in the case of mutations, melanocytes can begin to divide uncontrollably, leading to the formation of malignant tumors.
Melanoma is dangerous because it can metastasize, spreading to internal organs, which significantly reduces the chances of successful treatment. A tumor detected in time can be effectively treated, so it is important to know its main signs and causes.
Causes of occurrence
The main cause of melanoma is prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation from both sunlight and artificial sources such as tanning beds. However, not all cases of melanoma are UV-related; genetic factors also play an important role.
Genetic predisposition can also be a cause of melanoma. People who have a family history of melanoma are at a higher risk. Additional risk factors include having a large number of moles on the skin, especially those that are irregularly shaped or change over time. Melanoma can develop even in people who have not had significant exposure to sunlight, which emphasizes the importance of regular skin examinations.
Types of melanoma
There are several types of melanoma, each with different growth patterns and rates of spread.
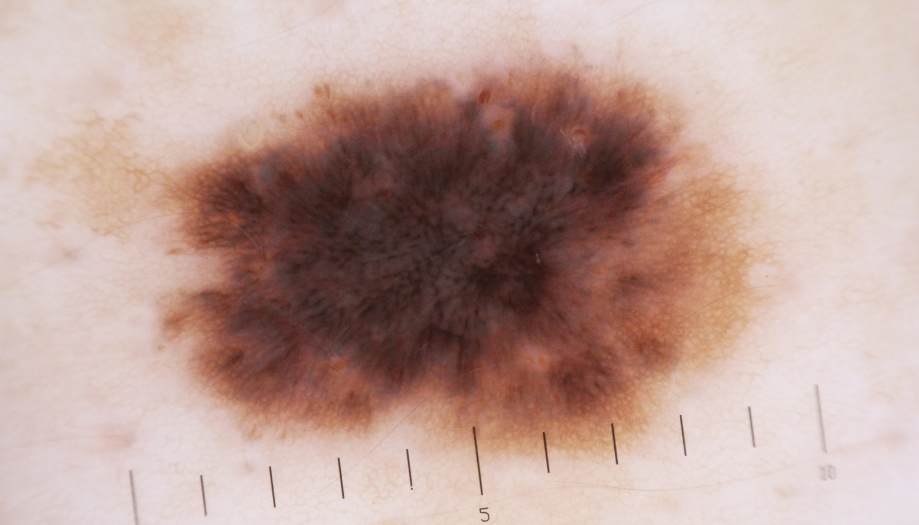
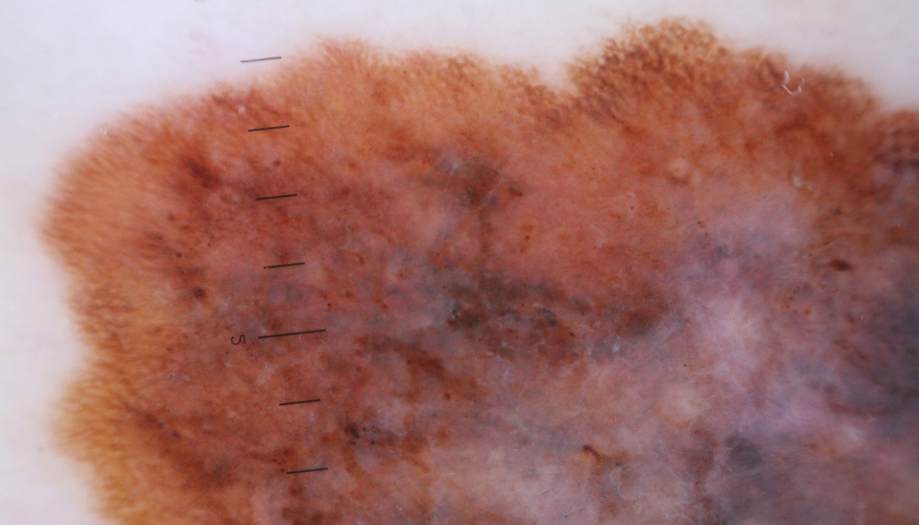
Melanoma under the microscope:
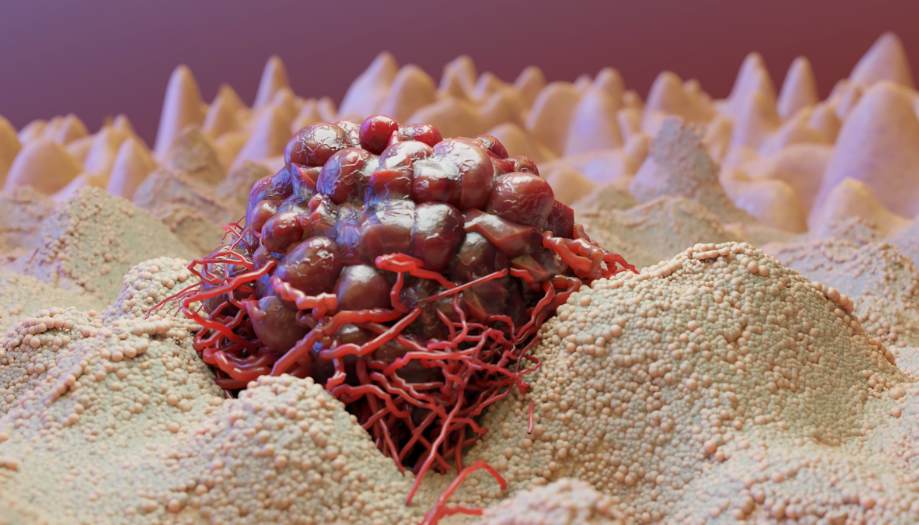
- Superficial spreading melanoma. This is the most common type, occurring in 70% of patients. It develops on the surface of the skin, often in areas that have been exposed to the sun. This type of melanoma can grow slowly over months or even years, remaining flat and unnoticeable before it begins to grow deeper.Superficial spreading melanoma.
- Nodular melanoma. It is characterized by an aggressive course and growth rate. This type of tumor grows rapidly in depth and is more often detected in the late stages. Nodular melanoma often appears as a bulging mass that can be black, blue, or red in color.
- Lentigo melanoma. Usually found in older people and develops on exposed areas of the skin, such as the face and hands. This type of melanoma is also slow-growing but can eventually penetrate deep into the skin.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma. This rare type of tumor develops on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, or under the fingernails. It is more common in people with darker skin and is more difficult to diagnose because it appears on areas of the body that are less likely to be checked.
Risk factors
The risk of developing melanoma depends on many factors, both external and genetic.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The most significant risk factor is prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation, especially during childhood and adolescence. Frequent exposure to the sun without the use of protection, such as sunscreen and clothing, increases the likelihood of developing melanoma.Exposure to ultraviolet radiation
The most significant risk factor is prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation, especially during childhood and adolescence. Frequent exposure to the sun without the use of protection, such as sunscreen and clothing, increases the likelihood of developing melanoma. - Genetic factors. The presence of melanoma in close relatives increases the risk of developing it. This is due to the fact that some mutations in genes can be inherited and cause a tendency to skin cancer.
- Light skin and predisposition. People with fair skin, blond or red hair and blue eyes are more at risk of developing melanoma. This is because they have less melanin in their skin, which provides protection from ultraviolet rays.
- History of skin disease. If a person has already had other skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, the risk of developing melanoma is greatly increased.
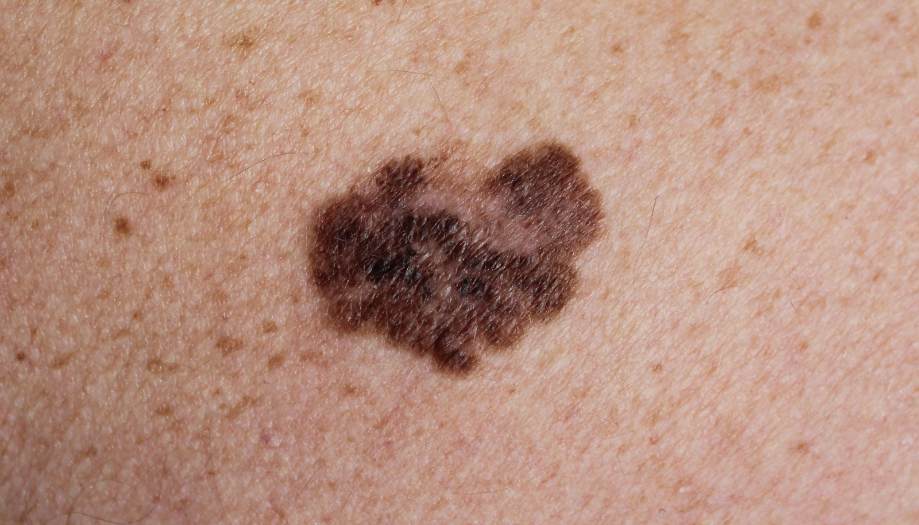
Признаки и симптомы меланомы
One of the keys to successful treatment of melanoma is early detection. There are several signs that may indicate the development of melanoma:
- Changes in the color of a mole. Moles that begin to change color or become irregular may be a sign of melanoma. Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of shades of black, brown, blue or red.
- Changes in shape and size. Increased size, uneven edges and asymmetry of moles are also possible signs of melanoma. It is important to watch for any changes in the contour and structure of the mole.
- Bleeding and itching. Moles that begin to bleed, itch or cause discomfort require immediate medical evaluation, as these symptoms may indicate malignant degeneration.
- Signs of late stages. In advanced stages, melanoma can spread to lymph nodes and internal organs. Symptoms may include weight loss, chronic fatigue, and pain in the affected areas of the body.
Diagnostic methods
Early diagnosis of melanoma significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. Modern medicine offers several effective methods for detecting this type of skin cancer.
- Skin self-examination. Regular skin examinations play a key role in the early diagnosis of melanoma. It is important to check all moles for changes in color, shape, size, or texture. Doctors recommend self-examination at least once a month. Using the ABCDE rule helps people spot potentially dangerous moles:
- A (Asymmetry) – asymmetry in the shape of the mole.
- B (Border) – uneven or blurred edges.
- C (Color) – color change or the appearance of multiple shades.
- D (Diameter) – diameter greater than 6 mm.
- E (Evolving) – changes over time (size, shape, color).
- Dermatoscopy. This is a non-invasive method, during which the doctor uses a special magnifying device for a more detailed examination of skin formations. This method helps to get a better look at the structure of the mole and detect early signs of malignancy.
- Biopsy. If your doctor suspects melanoma, a biopsy – taking a small sample of skin for further laboratory analysis – may be ordered. There are several types of biopsies, including:
- Пункционная биопсия – забор небольшого фрагмента кожи из подозрительного участка.
- Excisional biopsy is the complete removal of a suspicious mass for the purpose of examination. The biopsy can accurately determine whether the tumor is malignant and determine its type and stage.
- Genetic testing. In some cases, doctors may recommend genetic testing, especially if the patient or relatives have a history of melanoma. This helps to detect the presence of mutations in genes associated with a high risk of developing skin cancer.
Stages of melanoma development
Melanoma is classified into stages depending on the depth of penetration and the extent of tumor spread. There are five main stages:
- Stage zero (in situ). At this stage, the melanoma is exclusively in the top layer of skin (epidermis) and has not yet spread to the deeper layers of the skin. This is the least dangerous stage, in which surgical removal of the tumor gives almost complete recovery.
- Stage one. Melanoma begins to penetrate into deeper layers of the skin, but its thickness does not exceed 1 mm. At this stage, metastasis to lymph nodes and other organs does not occur, and the chances of recovery remain high.
- Stage two. The tumor increases in size and can reach up to 4 mm in thickness. At this stage, the first signs of damage to nearby tissues may appear, but there are no metastases yet.
- Stage three. The melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes. This makes treatment much more difficult and requires more aggressive therapies such as immunotherapy or chemotherapy.
- Stage four. At this stage, melanoma metastasizes to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, or brain. Treatment becomes much more complex, and prognosis depends on the patient’s general condition and the effectiveness of the chosen therapy.
Melanoma treatment
The treatment of melanoma depends on its stage, type and general health of the patient. In most cases, it involves a combination of several methods.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ S urgical removal | The main treatment for melanoma. The tumor is excised along with the surrounding healthy tissue. In later stages, nearby lymph nodes may be removed. |
| ✅ Mohs micrographic surgery | Removal of the tumor layer by layer with microscopic examination of the tissue. It is used for non-melanoma tumors, but is sometimes used for melanoma. |
| ✅ Radiation therapy | The use of high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Used after surgical removal or to treat metastatic melanoma. |
| ✅ Chemotherapy | Treatment with anti-cancer drugs. Most often used in the late stages of melanoma when the cancer has spread beyond the skin. |
| ✅ Immunotherapy | Activation of the immune system to fight cancer cells. Particularly effective in advanced stages of melanoma. |
| ✅ Targeted therapy. | Drugs aim to block mutations in melanoma cells, which stops them from growing and multiplying. It is used in the presence of specific mutations. |

The need for melanoma removal
Melanoma removal is a key step in the treatment of this type of skin cancer. It is important to realize that in the early stages, surgery can provide a complete cure. If melanoma is not removed in a timely manner, it can begin to spread deep into the skin and metastasize to lymph nodes and other organs, making treatment much more difficult.
- Why is it important to remove melanoma in its early stages? Melanoma is an aggressive form of cancer that spreads rapidly throughout the body. In the early stages, melanoma is confined to the skin, and surgical removal of the tumor can completely eliminate the cancer cells, preventing further spread. The prognosis in the early stages is usually very favorable, with a high probability of complete recovery.
- What happens if melanoma is not removed? If left untreated, melanoma will begin to grow deep into the skin and infiltrate blood and lymph vessels. This leads to metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells to other organs. In advanced stages, melanoma can affect vital organs such as the lungs, liver and brain, which significantly reduces the chances of successful treatment and can be fatal.
- Risks of recurrence after removal Even after melanoma removal, there is a chance of recurrence, especially if the tumor was at an advanced stage. To reduce the risk of recurrence, doctors may prescribe additional treatment such as radiation or immunotherapy. Regular checkups with a dermatologist after treatment are also an important part of relapse prevention.
Laser removal of melanoma: is it possible?
Laser removal of melanoma is not a standard treatment. The reason is that the laser cannot completely remove all cancer cells deep under the skin, which can lead to recurrence or further spread of the tumor. Melanoma is an aggressive form of cancer and its treatment requires more radical methods that guarantee complete removal of the malignant tissue.
Why is laser not used to remove melanoma?
Laser procedures are effective for removing benign skin growths such as papillomas, moles or warts, but melanoma requires a more radical approach. Laser cannot guarantee complete removal of all cancer cells, especially if the tumor has already penetrated deep into the skin or spread to other areas of the body. In addition, the laser may worsen the diagnosis by making the tumor less visible, making further treatment more difficult.
Is laser removal of moles before melanoma is allowed?
Laser removal of moles is acceptable and widely used to eliminate benign neoplasms on the skin. However, it is very important that the mole be examined by a dermatologist or oncologist before the procedure to rule out its malignant nature. If the mole shows signs of possible melanoma, laser removal is not recommended as it can complicate the diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer.

Why is it important to examine moles before laser removal?
- Risk of hidden malignant changes Even if a mole looks harmless, it can sometimes contain hidden signs of melanoma or other forms of skin cancer. Before any cosmetic procedures, it is important to undergo a diagnostic test to rule out the presence of cancer cells. A dermatologist may recommend a biopsy or other diagnostic test.
- Laser can hide melanoma. The laser removes the top layers of skin, and this can make diagnosing melanoma more difficult. If malignant changes have already begun in the mole, laser removal will not be able to determine how deep the tumor has spread, making further treatment more difficult.
When is laser mole removal safe?
Laser mole removal is safe in cases where the neoplasm is benign and does not carry a risk of turning into melanoma. Such procedures are performed to improve the appearance of the skin, as well as to eliminate the inconvenience that can cause large or protruding moles (for example, rubbing with clothes). It is important that the decision about laser removal is made only after consultation with a doctor.
Which moles should be removed?
- Benign neoplasms. Moles that do not change in shape, color, or size are generally considered benign and can be removed by laser. However, even these should be examined by a doctor before the procedure.Benign neoplasms
Moles that do not change in shape, color, or size are generally considered benign and can be removed by laser. However, even these should be examined by a doctor before the procedure. - Moles that cause discomfort. Moles that rub or are frequently traumatized (e.g., on the neck, under the arms, or areas where they may be caught by clothing) can be safely removed by laser after it has been confirmed that they are benign.
GET YOUR MOLE CHECKED ONLINE RIGHT NOW

Melanoma prevention
While some risk factors for melanoma, such as genetic predisposition, cannot be changed, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the likelihood of developing it.
- Proper UV protection. One of the most effective ways to prevent melanoma is to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV rays. It is important to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially during its peak hours (10:00 to 16:00). Using sunscreen with a high SPF (at least 30) and wearing protective clothing can also help reduce the risk of melanoma.Proper UV protection
One of the most effective ways to prevent melanoma is to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV rays. It is important to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially during its peak hours (10:00 to 16:00). Using sunscreen with a high SPF (at least 30) and wearing protective clothing can also help reduce the risk of melanoma. - Use of sunscreen. Sunscreen should be applied to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days, as UV rays can penetrate through clouds. Apply the cream 15-30 minutes before going outdoors and renew every two hours, especially after swimming or heavy sweating.
- Regular checkups with a dermatologist. People at increased risk of melanoma (for example, those with fair skin or a family history of skin cancer) should see a dermatologist regularly for skin checks. This will help detect potential changes early, when treatment is most effective. Your doctor may recommend dermatoscopy or other diagnostic methods for more accurate monitoring.
Tips for skin care after melanoma removal
After surgical removal of melanoma, the skin requires special care to promote healing and prevent possible complications.
- How do I care for my wound after surgery? After surgery, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for wound care. This usually involves changing dressings regularly, using antiseptics to prevent infection, and minimizing physical activity that can damage the healing tissue. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection.
- Ways to prevent the appearance of new melanomas. Melanoma patients should take special care of their skin, as they are at an increased risk of developing new tumors. It is important to avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays, use sunscreen and have regular check-ups with a dermatologist. It is also recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and smoking cessation.
- Restoring and maintaining healthy skin. After melanoma removal, it is important to take care of your skin’s health by ensuring it is adequately moisturized and nourished. The use of special scar healing creams will help minimize scarring and speed recovery. It is important to avoid traumatizing the surgery area and protect it from the sun.
Early diagnosis and the importance of preventive examinations

Early diagnosis is a key factor in the successful treatment of melanoma. When a person understands what melanoma is and the earlier the disease is detected, the higher the chances of a full recovery.
- The importance of early diagnosis in successful treatment. If melanoma is detected in its early stages (stage zero or stage one), treatment may be limited to surgical removal without the need for additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This reduces the risks of complications and recurrence.
- How often should I be seen by a dermatologist? People at high risk of melanoma are recommended to see a dermatologist at least once a year for a complete skin exam. Those who have already had melanoma should be seen every 3 to 6 months for the first few years after treatment and then annually thereafter.
You now know What is Melanoma Melanoma is a dangerous cancer that requires attention and timely treatment. Early diagnosis and removal of the tumor can save your life, especially if the melanoma is detected at an early stage. Don’t forget about prevention: protect your skin from the sun, have regular check-ups with your dermatologist and monitor the condition of your moles. In case of any changes, do not delay a visit to the doctor. In Coolaser Clinic in Kiev you can undergo diagnosis and get a referral for melanoma treatment in the oncology center, which will help you to stay healthy and avoid serious consequences.
Sources: