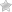Types of Scars: Top 4 types, Categories, Classifications and Varieties
Scars are not only physical Marks on the Skin, but also emotional Marks that Events in our lives Leave behind. They can be a Source of Shame and insecurity as Well as a Symbol of Strength and Endurance. In this Article, we will look at the different Types of Scars, their causes, Treatment and care Options, and the importance of emotional Acceptance.

Every Scar has a Story associated with Events that have left their Mark on the Skin. From Scary Burns to surgical Scars, they are an integral Part of the human Experience.
- Types of Scars: Top 4 types, Categories, Classifications and Varieties
- Characteristics of Scar tissue and how they Differ from Healthy Skin
- What are the main 4 Types of Scars
- Normotrophic Scars: their difference from all others
- Varieties of Atrophic Scars
- Classification of Acne Scars according to the Ice Pick Scars scale (Icepick Scars)
- Classification of Scars – Stretch Marks
- Classification of Kelloid Scars
- Classification of Scars with regard to their Characteristics and Origin
What are scars and scarring?
Scars are tissue that replaces skin damaged by injury or surgery. They form as a result of the natural wound healing process when the body begins to repair damaged tissue.
Characteristics of Scar tissue and how they Differ from Healthy Skin
| Characterization | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure and texture | – Denser and less elastic structure. – Uneven texture with bumps or depressions. |
| Color | – Different from surrounding healthy skin. – May be reddish, pink, white, or hyperpigmented. |
| Functionality | – Less functional: reduced sensitivity and protective function. – May lead to decreased skin flexibility. |
| Risk of recurrence | – Increased risk of recurrence in the same location. – Associated with altered scar tissue structure. |
| Absence of sweat glands | – Sweat glands are absent, reducing the ability to regulate body temperature. |
| The absence of hair follicles | – Hair follicles are absent and no hair grows in this area. |
| Collagen Fiber Structure | – The orientation of collagen fibers can be random. – More rigid and less flexible structure. |
This table helps visualize the differences between scar tissue and healthy skin. The main characteristics and distinguishing features of each tissue type are highlighted here.
What are the main 4 Types of Scars
There are several types of scars, each with its own characteristics and manifestations. Here are the main 4 types of scars:
| Type of scar | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ Atrophic | Depressed scars, which most often occur after advanced trauma or surgery. |
| ✅Normotrophic | Scars that are about the same height and texture as the surrounding skin. |
| ✅Hypertrophic | Bulging scars that can be itchy and painful. They usually do not extend beyond the initial wound. |
| ✅ Keloid | Scars characterized by overgrowth of tissue and often extending beyond the original wound. |

The type of Scar that forms is influenced by several Factors, including:
- depth
- the nature of the trauma,
- individual characteristics
- genetic predisposition
For example, Atrophic Scars are most often caused by deep or deep trauma. Especially when a significant portion of the dermis is damaged. Hypertrophic and Keloid Scars can form due to excess collagen formation during the healing process. Excess Collagen can be caused by a variety of factors, including heredity and the intensity of the inflammatory Process.
Causes of Scarring
Scars can occur from a variety of causes, including injuries, surgeries, burns, and even insect bites. They are the result of the skin’s natural healing process as it begins to recover from an injury.
Normotrophic Scars: their difference from all others
A normotrophic scar differs from other types of scars in several characteristics:
Appearance:
A normotrophic scar is usually flatter and less pronounced than other types of scars, such as hypertrophic or keloid scars.
It often barely stands out on the surface of the skin and can look like normal skin, although it may be slightly paler or darker.
Texture:
A normotrophic scar usually has a smoother and more uniform texture compared to other types of scars, which may be more uneven or bulging.
Size:
The size of a normotrophic scar is usually more compact and smaller than hypertrophic or keloid scars, which may extend beyond the original wound.
Symptoms:
Normotrophic scars are usually not accompanied by severe itching or soreness, which is typical of hypertrophic and keloid scars.
In general, a Normotrophic Scar is characterized by a less severe appearance and Symptoms compared to other Types of Scars. It is often considered the Most Natural and least noticeable of All Scar Types.
Varieties of Atrophic Scars
Atrophic Scars can have several Varieties. This depends on the cause and characteristics of the injury or surgery that led to their formation. Some of the types of atrophic scars include:

- Excision scars. Formed after surgical removal of a skin defect or tumor. They may have a depressed characteristic and may be just above or below the surrounding skin.
- Acne scars. Appear after acne rashes, especially in cases where inflammation has penetrated deep into the skin. They can be shallow or deep, and most often have an uneven or wavy texture.
- Pixel scars: These form after the application of laser treatments such as fractional laser rejuvenation. They may be shallow and have a fine texture.
- Injection scars. Can form after injections into the skin, such as hyaluronic acid or botulinum toxin injections. They can be small or large, depending on the characteristics of the injection and the body’s response to it.
- Stretch marks (stretch marks, striae). They appear as a result of stretching of the skin, such as during pregnancy or sudden weight changes. They may be linear or patchy and may be lighter or darker in color than the surrounding skin.
Classification of Acne Scars according to the Ice Pick Scars scale (Icepick Scars)
This classification refers to one type of atrophic scarring and describes scars with narrow, deep ulcers that look like the marks of a sharp ice pick or needle. These scars often look like small, narrow holes in the skin that may look like puncture marks.

This type of scarring is usually caused by deep inflammation in the hair follicles, which destroys the surrounding tissue and leaves ulcerated marks as it heals. Scars on the surface of the skin are usually 1 to 2 mm wide.
Characteristics of the Ice Pick Scars:
- Depth: Scars are characterized by deep depressions that penetrate deep into the skin. This makes them particularly noticeable and difficult to treat.
- Narrowness: Holes in the skin are usually narrow and 1 to 2 mm in diameter. They may appear as shallow indentations or puncture marks.
Causes of IcePick Scars formation:
- Deep inflammation: This type of scarring is often caused by deep inflammation in the hair follicles, which destroys the surrounding tissue as it heals.
Ice Pick Scars Treatment:
- Laser Therapy: One of the most effective treatments is laser therapy, which can reduce the depth and visibility of scars.
- Chemical Peels: The use of chemical peels can help improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of scarring.
- Micro-needling therapy: This treatment involves the use of fine needles to stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture.
Classification of Scars – Stretch Marks
The classification of striae (stretch marks) includes several types of scars, taking into account their characteristics and degree of severity:
- Red Stretch Marks (erythematous striae): Newly formed strictures that are usually bright red or purple in color. They usually appear first and may be more noticeable on light-colored skin.
- White Stretch Marks (albino striae): Striae that have already passed the inflammation stage and have taken on a lighter or whiter color. They most often occur after the skin has recovered from a stretch mark.
- Atrophic Stretch Marks: Striae that are characterized by a depressed or concave appearance on the surface of the skin. This is due to a loss of skin elasticity in the area of the striae.
- Hypertrophic Stretch Marks: Less common, they are characterized by a more protruding, thicker and tougher skin texture in the area of the striae.
- Combined Stretch Marks: May include mixed characteristics of red and white striae, as well as elements of atrophic and hypertrophic Scars.
Classification of Kelloid Scars
The table describes the types of keloid scars:
| Characterization | Description |
|---|---|
| Place of education | – Keloids on the face: Scars that form on the face can be particularly noticeable and cause aesthetic dissatisfaction. – Keloids on the body: Can occur on other parts of the body, such as the chest, back, or limbs, and can also attract attention because of their size and shape. |
| Size and shape | – Small keloids: Relatively small scars with a diameter of a few millimeters to a few centimeters. – Large keloids: Scars with significant size, spreading over a large area of skin, sometimes reaching several tens of centimeters in diameter. |
| Degree of symptomatology | – Asymptomatic keloids: They are accompanied by itching, pain or discomfort, which can significantly affect the patient’s quality of life. – Asymptomatic keloids: They are less noticeable and do not cause physical or emotional discomfort. |

Classification of Scars with regard to their Characteristics and Origin
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| By shape and size | – Round or oval scars: These are circular or oval in shape and can be of various sizes. – Linear scars: They extend along the skin surface and can be short or long. – Irregularly shaped scars: They can have indeterminate or unusual shapes. |
| Because of the formation | – Trauma Scars: Occurs as a result of physical trauma such as a wound or surgery. – Burn Scars: Occurs as a result of a burn injury to the skin. – Acne Scars: Occurs as a result of inflammation caused by acne or blackheads. |
| In terms of severity | – Superficial scars: Are on the surface of the skin and may be less noticeable. – Deep scars: Penetrate deep into the skin and may be more visible and difficult to treat. |
| Symptomatically. | – Symptomatic scars: Are accompanied by itching, pain or other discomfort. – Asymptomatic scars: Do not cause physical or emotional distress to the patient. |
Factors affecting scar formation
Scar formation depends on a variety of factors, including genetics, age, and skin type. Here is a more detailed description of these factors with facts and figures:
- Genetic features:
- Genetics plays an important role in the propensity for scarring. In some people, genes may predispose them to more scarring during wound healing.
- Research shows that heredity can have a strong influence on skin regeneration and scar formation. For example, a study conducted at the University of Oxford showed that up to 60% of individual differences in the propensity to scar formation can be explained by genetic factors.
- Age:
- Age can also affect the wound healing process and scar formation. Children’s skin has a greater ability to regenerate and usually heals faster and with less scarring than adults.
- As we age, there is a natural decline in fibroblast activity and collagen production, which can lead to more visible scarring. According to a study published in the journal Dermatologic Surgery, people over the age of 40 have an increased risk of scarring compared to younger patients.
- Skin Type:
- Skin type also influences the healing process and scar formation. For example, people with oily skin are more prone to hypertrophic and keloid scarring due to increased sebum production and risk of inflammation.
- Statistics presented in the journal Archives of Dermatology indicate that people with oily skin have a 15 times higher risk of developing keloid scars than people with normal or dry skin.
These factors are key in determining the propensity for scar formation and may help to understand why some people may have more visible and pronounced scarring than others.
Conclusion
Scars and scars are an integral part of our lives, but they do not define our beauty and worth. It’s important to accept your scars and see them as having emotional value as well as physical. And remember that the story of each scar is the story of your strength and endurance.
Coolaser Clinic in the center of Kiev on Pechersk takes care of the beauty and health of your skin.
Types of Scars: what scars and scars are – today our experts have shared the most essential information with you, stay healthy!
Sources: